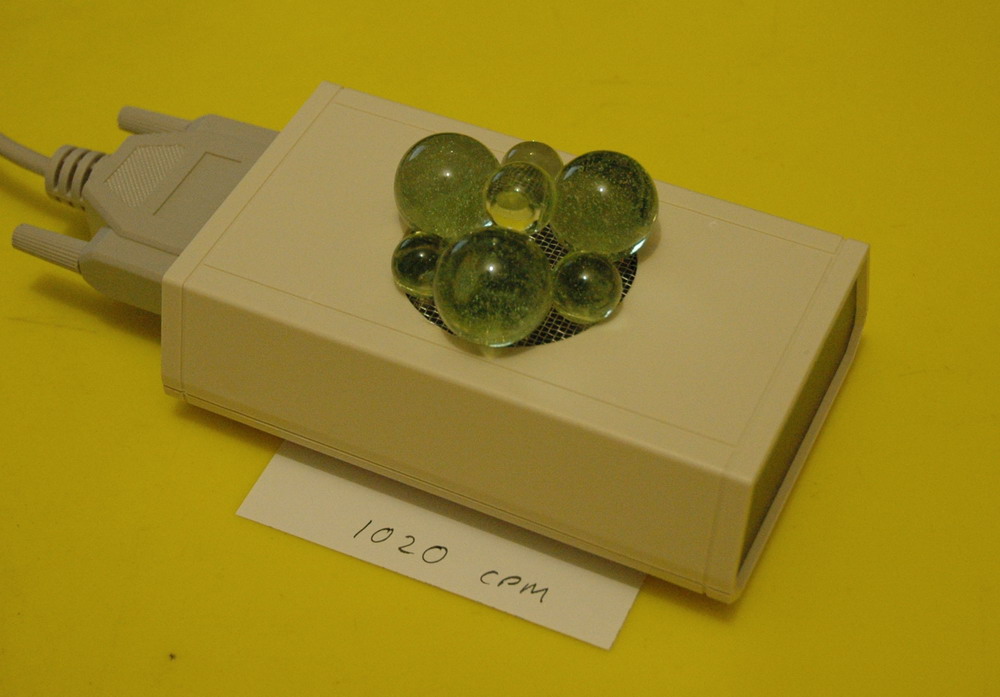
Potassium has some natural beta radiation (high speed electrons or positrons) and can penetrate paper but not a few mm of aluminium.
“Continue reading” to read about Cherenkov radiation, tritium, antineutrinos and links…
Potassium chloride 50% here is from the “reduced sodium salt” version of table salt. The count is 238 through paper. Background radiation is 50 CPM.
Potassium-40 is the main radioactive isotope with one part in 10,000 (0.0117%) abundance. It decays with a half life of a billion years (1.248×109 y).
It can decay by three methods:
Firstly (90%), by decay to calcium-40 with beta particle of 1.33 MeV which is the most common path and what is seen here. Also an electron antineutrino.
Secondly (10%), by electron capture to argon-40 with a gamma particle and neutrino.
Thirdly and rarely, it can decay to argon-40 with a positron and a neutrino.
Potassium decay to argon is interesting. Argon-40 constitutes about 1% of the atmosphere. Since the sun’s argon is argon-36 this means that 1% of the air you breath is a potassium radioactive by product.
Blue Cherenkov radiation light is seen near control rods in water in a nuclear reactor. This is due to beta radiation travelling faster than the speed of light IN WATER. This speed is only 75% of the speed of light in a vacuum.
Tritium also decays by beta radiation.
Related pages
Try something else
External links
Beta radiation – Wikipedia
Potassium-40
Photo Date:2006